This blog post aims to unfold the details of DPI, exploring its definition, methods, applications, modern technologies, and the challenges it presents in the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity.
Introduction to DPI
Deep packet Inspection (DPI) is a technique in network traffic monitoring which is an essential part of the computer network field. Simply, packet inspection is the process of extracting details from network packets and use those details for purposes such as; identifying trends, catogorizing traffic into applications, anomaly detection, cyber attacks detection and so on.
When it comes to the DPI, it is a more sophisticated technology than normal packet inspection. It plays a crucial role in understanding, analyzing, and managing the complex flow of data across networks. In the vast landscape of network security and traffic management, one term that frequently surfaces is DPI.

In this blog post, we will dive into the depths of Deep Packet Inspection, exploring its definitions, methods, and diverse applications.
Understanding Deep Packet Inspection
Deep Packet Inspection, often abbreviated as DPI, is a technology that enables the inspection and analysis of the content of data packets as they traverse a network. Unlike traditional packet inspection, which focuses on the header information of packets, DPI dives into the payload, scrutinizing the actual data being transmitted.
Packet inspection can be categorized into two parts as:
-
Shallow Packet Inspection
Analyze upto layer 4 of OSI Layer model.
-
Deep packet Inspection
Analyze up to layer 7 in OSI model (Visibility of all the layers).
This granular level of examination provides a wealth of information about the nature and purpose of the data.
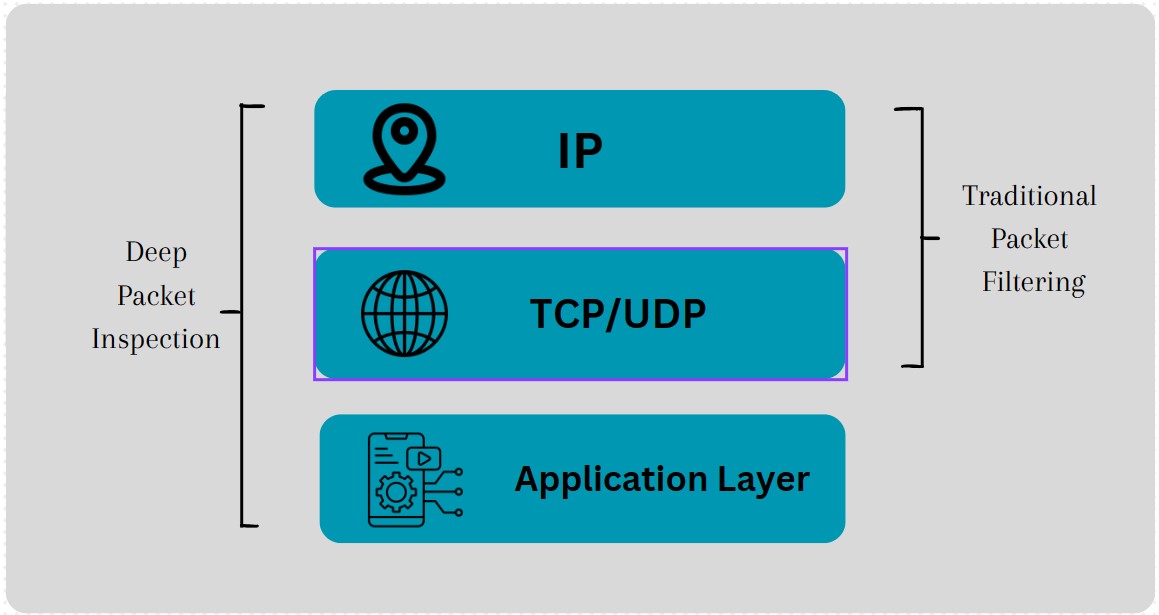
Conventional Packet Filtering vs. Deep Packet Inspection
Conventional Packet Filtering
Conventional packet filtering (Shallow Packet Inspection) primarily examines the header information of data packets, making decisions based on source and destination addresses, ports, and protocols.
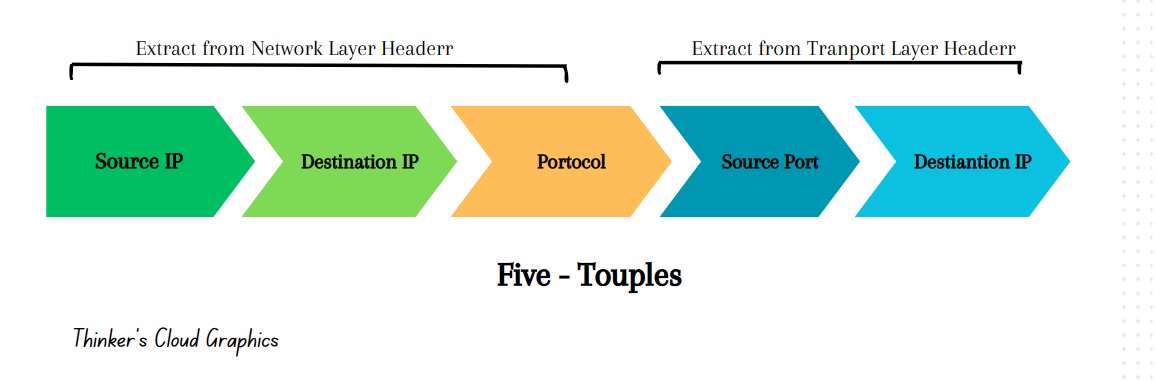
Using the above 5 details, we can categorize all the packets travessing trough a network into sessions. A session is a packet exchange between two entities having above five-touple fixed during the sessoin.
- Five Touple
- Source IP address
- Destination IP address
- Source Port
- Destination Port
- IP protocol
It operates at the network layer of the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model and is effective for basic traffic categorization as sessions for the purposes of basic traffic analytics and control but lacks the depth required for detailed analysis.
Deep Packet Inspection
DPI goes beyond header information; dig into the payload or content of data packets. This granular inspection allows for a thorough understanding of the data being transmitted. By operating at the application layer of the OSI model, DPI provides insights into the specific applications and services generating the traffic.
Methods of Deep Packet Inspection
1. Signature-Based Inspection
This is one of the basic methods identifies that known patterns or signatures within packet payloads, enabling the detection of specific applications, protocols, or threats.
Here, the content of the packets is compared against a database of predefined signatures. These signatures represent patterns associated with known applications, threats, viruses, malware, or other undesirable content.
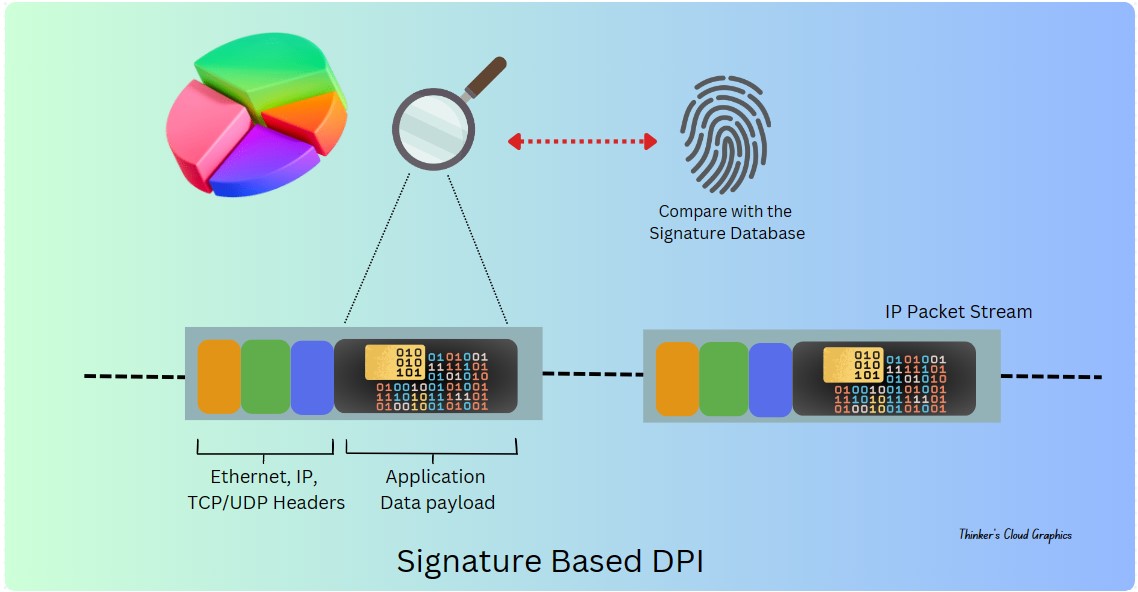
Basically, this acts as mapping a set of bytes against a known byte pattern. Those signatures need to be updated regularly according to new applications or new threats by network engineers.
2. String Matching Analysis
Many applications have textual identifiers that are contained within the payload part of the IP packets. We can use those specific words or phrases to identify the applications and even extract more sophisticated details of the users as well. (http request packets: user agent string contains Device info; Model, OS, Browser,..etc.)
3. Heuristic-Based Inspection
Uses algorithms and rules to identify deviations from normal patterns, allowing the detection of previously unknown threats or anomalies. Here we are defining a set of rules which can be used to clearly identify normal vs. abnormal behavior of sessions.
4. Behavioral Analysis
Monitors and analyzes the behavior of network traffic over time, establishing baselines for normal behavior and detecting unusual patterns.
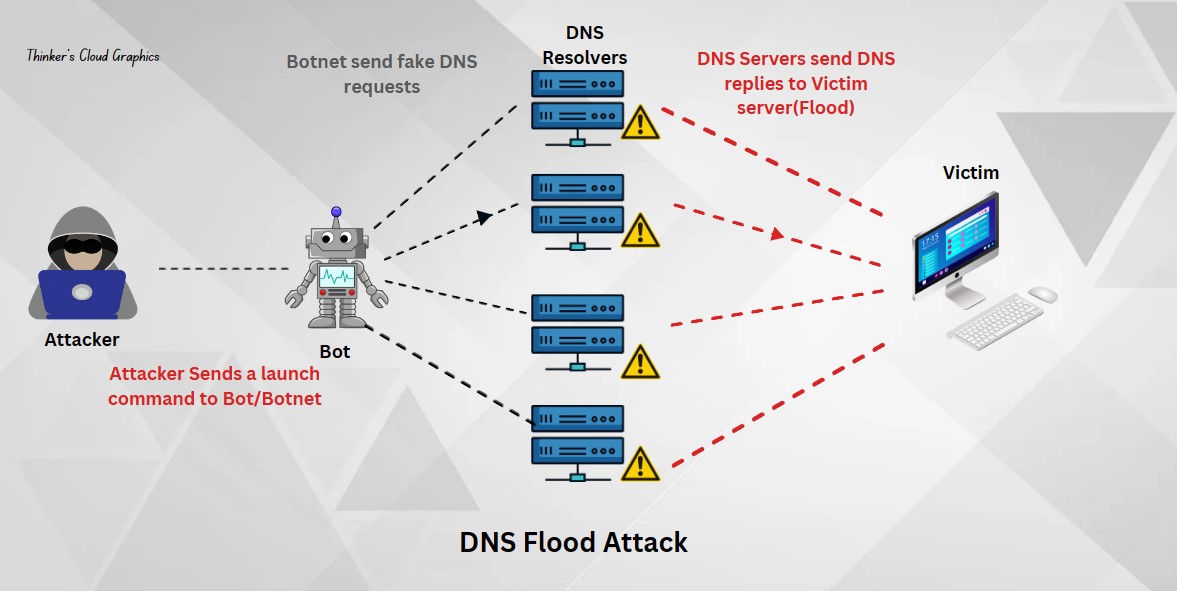
This is helpful to identify possible threats within a network such as cyber attacks. Ex: Whenever a DoS(Denial of Service) or DDoS(Distributed Denial of Service) attack happens, it can cause an unusual behaviour such as abnormally high amount of DNS requests (DNS floods), so suspicios traffic originating from a single IP or a subnet and sudden increment in bandwidths.
5. Numerical Property Analysis
There are many other properties that we can track with the time related to the statistics of network sessions such as
- packet/payload sizes
- Packet Timing
- Throughput
- Connection Duration
By monitoring the trends of those properties over time, we can come up with analytic conclusions about the sessions. This can help in identifying patterns or anomalies associated with certain types of traffic.
A Challenge for DPI “Data Encryption”
As encryption becomes more widespread, DPI faces challenges in inspecting encrypted traffic, leading to blind spots in threat detection. There are multiple encryption protocols and algorithms in use, such as TLS (Transport Layer Security) for web traffic and end-to-end encryption in messaging applications. Those are really challenging situations for DPI since the deeper details cannot be extracted using the ecrypted payload with many of the existing DPI techniques.
Modern Technologies of DPI
Machine Learning and AI for DPI
DPI leverages machine learning algorithms and artificial intelligence to enhance its ability to identify and respond to evolving threats.
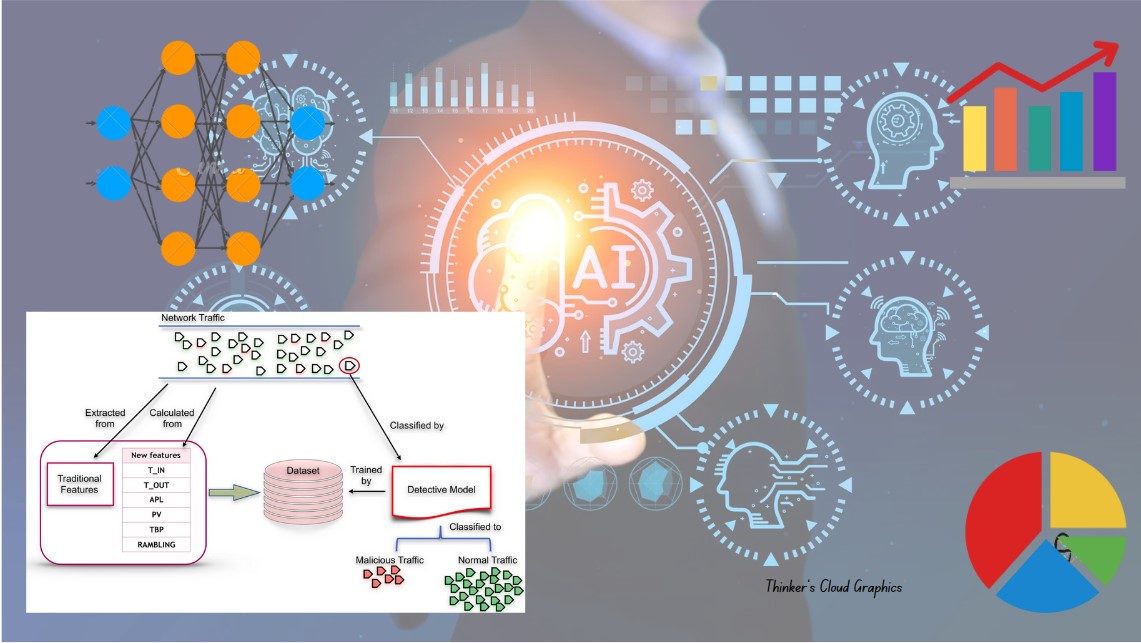
Machine learning algorithms enable the classification of network traffic by training models on known categories. These models can automatically identify and classify new traffic. Common algorithms used for this purpose include decision trees, support vector machines (SVM), and Naive Bayes classifiers.
Additionally, ML can assist in the automatic generation of signatures for known threats or applications. By analyzing historical data and patterns, ML models can create signatures that can be used to detect similar traffic in the future.
SSL/TLS Interception
DPI has evolved to inspect encrypted traffic, decrypting and analyzing the content of SSL/TLS-encrypted packets to ensure the security of the network.
A Solution for HTTPS Encryption Some firewalls now offer HTTPS inspections (Firewall SSL/TLS Interception), which would decrypt the HTTPS-protected traffic and determine whether the content can pass through.
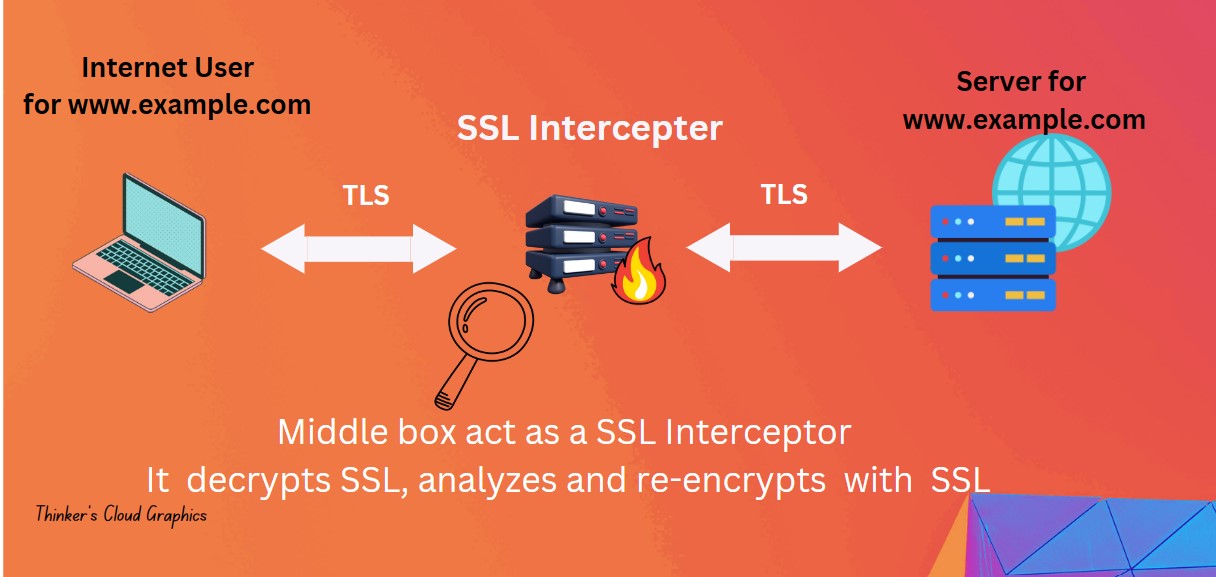
According to the above illustration,
- The middle box (a firewall) decrypts the incomming packets from the Server or the client using its own a dynamic SSL certificate.
- Then read the decrypted payload using above DPI methods and extract usefull information for application and threat detection.
- Finally, it re-encrypt the packet using a certificate and forward to the receiving end.
Users’ browsers must trust this certificate, which is usually signed by a local certificate authority (CA) configured on the security device.
Applications of DPI
Application Identification
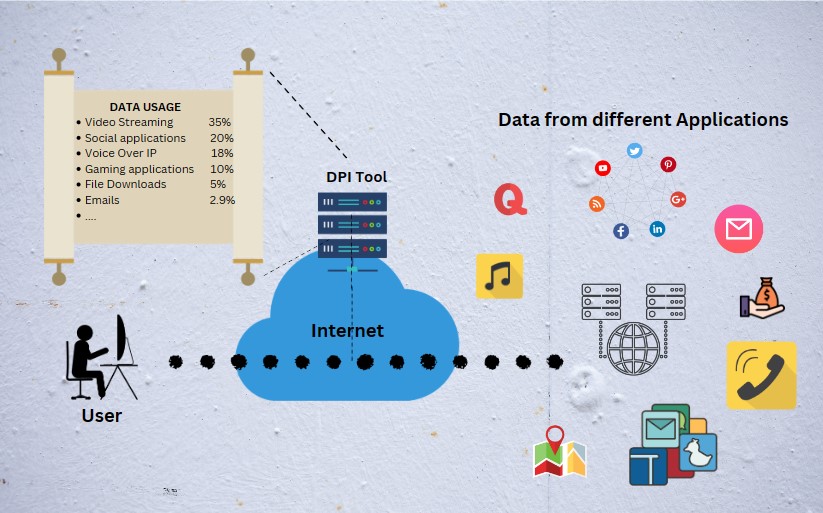
DPI classifies and identifies applications running on a network, offering insights into application-level traffic patterns and enabling policy enforcement. This is most common because application wise traffic and usage monitoring is an essential need of any ISP. (Ex: ISPs offer data packages with high priority for business critical applications )
Network Security
DPI is a cornerstone of modern network security, providing the ability to detect and mitigate various threats, including malware, intrusion attempts, and data exfiltration.
Quality of Service (QoS)
DPI is crucial for managing network traffic, ensuring optimal performance for critical applications by prioritizing and allocating bandwidth based on application needs.
Regulatory Compliance
DPI assists organizations in adhering to regulatory requirements by monitoring and controlling the content of data traversing the network.
Conclusion
Deep Packet Inspection has emerged as a pivotal technology in the area of network security and management. Its ability to extract the content of data packets at a granular level provides invaluable insights for securing networks, optimizing performance, and ensuring regulatory compliance. However, the adoption of DPI comes with challenges, including privacy concerns and the need to adapt to evolving encryption technologies. As we discuss on the the cybersecurity field, DPI stands as a powerful tool, continually evolving to meet the demands of an ever-changing technlogies.



Leave a comment